| Flags - #9 - History of your flag and others | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
Stage Nine of Flags - Learn and share with your group the history of your country/island’s flag and what the colors and symbols on it represent. Remember that you should have a notepad or printout of your worksheet. The worksheet is located at the lower part of your Flags Screen. If you do not have a printout then take notes so you can put the information needed in the boxes. Bermuda
The Flag of Bermuda was adopted on October 4, 1910 with a revision in 1999. The elements are:
Canada
Canadian Heritage is responsible for flag promotion and protocol. Explore their page here for everything you need to know about the Maple Leaf
United Kingdom All UK specific answers and other general info. http://www.flaginstitute.org/pdfs/Flying_Flags_in_the_United_Kingdom.pdf
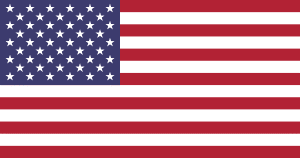
United States
The red and white stripes represent the original 13 colonies. The (current) 50 stars represent the current 50 states, the number being increased as states were added.
Burundi Flag of Burundi The national flag of Burundi was adopted on June 28, 1967 after the country's independence from Belgium on 1 July 1962. It consists of a white saltire which divides the field into alternating red and green areas. The center of the saltire merges into a white disk, on which there are three red solid six-pointed stars outlined in green. The flag is divided into four parts by a white cross. The upper and lower parts are red in color while the left and right ones are green in color. White color of the cross represents peace, green represents the nation's hopes placed on future development and red symbolizes the suffering of the nation during its freedom struggle.[2] The three stars in triangular configuration stand for the three major ethnic groups of Burundi: the Hutu, the Twa and the Tutsi.[2] The three stars also stand for the three elements of the national motto: Unité, Travail, Progrès ("Unity, Work and Progress"), which can be seen on the Coat of arms of Burundi.[3] They also represent the loyalty that the citizens of the nations have pledged to their God, king and country. Flag of Burundi
Rwanda Flag_of_Rwanda The flag of Rwanda was adopted on October 25, 2001. The flag has four colours: blue, green, and two forms of yellow[1] (standard yellow for the middle band and what the Pantone system calls "sun yellow" for the sun). The blue band represents happiness and peace, the yellow band symbolizes economic development, and the green band symbolizes the hope of prosperity. The sun represents enlightenment. The new flag represents national unity, respect for work, heroism, and confidence in the future. It was adopted to avoid connotations to the 1994 genocide. The flag was designed by Alphonse Kirimobenecyo. When hung vertically, the flag should be displayed as the horizontal version rotated clockwise 90 degrees. Flag of Rwanda
Zambia Flag_of_Zambia The flag of Zambia was adopted upon independence on October 24, 1964. Before that, Zambia was the British protectorate of Northern Rhodesia and used a defaced Blue Ensign as its flag. The current flag is used as both national flag and ensign. It is green with an orange-coloured African fish eagle in flight over a rectangular block of three vertical stripes, coloured, from left to right: red, black and orange. The placement of the eagle and block of stripes at the flag's fly is notable as most emblems and devices on flags are placed at centre or at the hoist. The colours used in the flag of Zambia are rich in symbolism. Green stands for the nation's lush flora, red for the nation's struggle for freedom, black for the Zambian people, and orange for the land's natural resources and mineral wealth. Additionally, the eagle flying above the coloured stripes is intended to represent the people's ability to rise above the nation's problems. The design of the national flag of Zambia is described in National Flag and Armorial Ensigns Act of 4 June 1965.[1] Green with an orange coloured eagle in flight over a rectangular block of three vertical stripes coloured from left to right in red, black and orange; of overall dimensions 3:2; and to the following colour specifications: "Spectrum Green", British Colour Council Shade reference 100. "Union Jack Red", British Colour Council Shade reference 210. "Jet Black", British Colour Council Shade reference 220. "Spectrum Orange", British Colour Council Shade reference 57. ColoursThe green was adjusted in 1996 to a lighter and brighter green. In 2012 The London Organising Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games solicited advice from each participating nation the correct Pantone colours for its flag. Once confirmed, the results were published in a guide. SymbolismThe flag's colours and emblems are rich in symbolism. Each of the four colours represents an aspect of Zambia: green for the country's natural resources and vegetation; red for its struggle for freedom; black for its people and orange for its mineral wealth (primarily copper). The eagle is an African fish eagle, which also appears in the national coat of arms and represents the people's ability to rise above the nation's problems. Flag protocolBy law, the Zambian flag should be flown only between the hours of sunrise and sunset and may be flown: - at buildings or premises owned or occupied by the Government; - at buildings or premises owned or occupied by local government authorities; - at buildings or premises owned or occupied by any statutory board or statutory corporation; - at state-aided schools; - on any motor car, boat or ship in or by which a Minister of Government is for the time being travelling; - on any ship registered as Zambian. The flag is not allowed to be flown by any other individual or institution without express written permission from the Minister except on the following occasions: - on the following public holidays, namely: Africa Freedom Day, Heroes Day, Unity Day, and Independence Day; - on such other days or occasions as the Minister may declare for this purpose. Flag of Zambia
South Sudan Flag_of_South_Sudan The flag of South Sudan was adopted following the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement that ended the Second Sudanese Civil War. The flag was previously used as the flag of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement. The flag bears striking similarities with those of Sudan (from whom Southern Sudan seceded in 2011), and Kenya. It shares the black, white, red, and green of the Sudanese flag (though different symbolism is given to the colours), in addition to having a triangle along the hoist. The horizontal black, white, red, and green bands, fimbriated white, are the same design as the Kenyan flag, and the Pan-African symbolism it conveys. - Black: Black African skin. - Red: Blood that was shed by the liberation struggle martyrs. - Green: The country's natural resources and verdant land. - White: Peace attained after many years of the liberation struggle. - Blue: Waters of the Nile River, a source of life for the country. - Yellow: The unity of the states making up South Sudan. Flag of South Sudan
Tanzania Flag_of_Tanzania The flag of Tanzania consists of a yellow-edged black diagonal band divided diagonally from the lower hoist-side corner, with a green upper triangle and blue lower triangle. Adopted in 1964 to replace the individual flags of Tanganyika and Zanzibar, it has been the flag of the United Republic of Tanzania since the two states merged that year. The design of the present flag incorporates the elements from the two former flags. The United Kingdo – together with its dominion South Africa and fellow Allied power Belgium – occupied the majority of German East Africa in 1916 during the East African Campaign. Three years later, the British were tasked with administering the Tanganyika Territory as a League of Nations mandate. It was turned into a UN Trust Territory after World War II, when the LN dissolved in 1946 and the United Nations was formed. In 1954, the Tanganyika African Association – which spoke out against British colonial rule – became the Tanganyika African National Union (TANU) under the leadership of Julius Nyerere and Oscar Kambona. The aim of the political party was to attain independence for the territory; its flag was a tricolour consisting of three horizontal green, black and green bands.Shortly before independence in 1961, elections were held in Tanganyika. After the TANU won comprehensively, the British colonial leaders advised them to utilize the design of their party's flag as inspiration for a new national flag. As a result, yellow stripes were added, and Tanganyika became independent on 9 December 1961. In April 1964, both Tanganyika and Zanzibar united in order to form a single country – the United Republic of Tanzania. Consequently, the flag designs of the two states were amalgamated to establish a new national flag. The green and black colours from the flag of Tanganyika were retained along with the blue from Zanzibar's flag, with a diagonal design used "for distinctiveness".[3] This combined design was adopted on 30 June 1964. It was featured on the first set of stamps issued by the newly unified country. SymbolismThe colors and symbols of the flag carry cultural, political, and regional meanings. The green alludes to the natural vegetation and "rich agricultural resources" of the country, while black represents the Swahili people who are native to Tanzania. The blue epitomizes the Indian Ocean, as well as the nation's numerous lakes and rivers. The thin stripes stand for Tanzania's mineral wealth, derived from the "rich deposits" in the land. While Whitney Smith in the Encyclopædia Britannica and Dorling Kindersley's Complete Flags of the World describe the fimbriations as yellow, other sources – such as The World Factbook and Simon Clarke in the journal Azania: Archaeological Research in Africa – contend that it is actually gold. Flag of Tanzania
Uganda Flag_of_Uganda The flag of Uganda was adopted on 9 October 1962, the date that Uganda became independent from the United Kingdom. It consists of six equal horizontal bands of black (top), yellow, red, black, yellow, and red (bottom); a white disc is superimposed at the centre and depicts the national symbol, a grey crowned crane, facing the hoist side. HistoryWhen the Democratic Party ruled the country, a design for flag was proposed. It had vertical stripes of green-blue-green, separated by narrower yellow stripes, and in the centre had the silhouette of a yellow crane. After the party lost the national elections on April 25, 1962 the newly elected Uganda People’s Congress (UPC) rejected the former design and instead proposed the current design. It was based on the flag of UPC– a tricolor having horizontal strips of red, yellow and black. The British administration gave their approval to this design before the country's independence. The flag was designed by the Ugandan Minister of Justice, Grace Ibingira. SymbolismThe three colours are representative of African peoples (black), Africa's sunshine (yellow), and African brotherhood (red being the colour of blood, through which all Africans are connected). The grey crowned crane is fabled for its gentle nature and was also the military badge of Ugandan soldiers during British rule. The raised leg of the crane symbolizes the forward movement of the country.
Democratic Republic of the Congo Flag_of_the_Democratic_Republic_of_the_Congo The flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a sky blue flag, adorned with a yellow star in the upper left canton and cut diagonally by a red stripe with a yellow fimbriation. It was adopted on 20 February 2006. A new constitution, ratified in December 2005 and which came into effect in February 2006, promoted a return to a flag similar to that flown between 1963 and 1971, with a change from a royal blue to sky blue background. Blue represents peace. Red stands for "the blood of the country's martyrs, yellow the country's wealth; and the star a radiant future for the country." Previous flagsThe previous flag was adopted in 2003. It is similar to the flag used between 1960 and 1963. The flag is based on the flag which was originally used by King Leopold's Association Internationale Africaine and was first used in 1877. The design was then implemented as the flag of the Congo Free State after the territory was recognized as an official possession of Leopold II at the Berlin Conference. After gaining independence from Belgium on 30 June 1960, the same basic design was maintained. However, six stars were incorporated to symbolise the six provinces of the country at the time. This design was used only from 1960 to 1963. The flag of the first Republic of Mobutu Sese Seko became the official banner after Mobutu established his dictatorship. This flag was used from 1966–1971 and consisted of the same yellow star, now made smaller, situated in the top corner of the hoist side, with a red, yellow-lined band running diagonally across the center. The red symbolized the people's blood; the yellow symbolized prosperity; the blue symbolized hope; and the star represented unity. This flag was changed when the country was renamed Zaire in 1971. The Zaire flag was created as part of Mobutu's attempted re-Africanization of the nation and was used officially until Mobutu's overthrow in the First Congo War. Flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
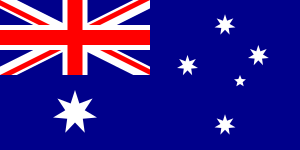
Australian Flag Flag of Australia The Australian National Flag (the flag) was first flown in 1901. It is Australia's foremost national symbol and has become an expression of Australian identity and pride.The flag is paraded by our defense forces and displayed around the country at sporting events and by service organisations, schools, community groups and private citizens. The flag has three elements on a blue background: the Union Jack, the Commonwealth Star and the Southern Cross. The Union Jack in the upper left corner represents the history of British settlement. Below the Union Jack is a white Commonwealth, or Federation, star. It has seven points representing the unity of the six states and the territories of the Commonwealth of Australia. The star is also featured on the Commonwealth Coat of Arms. The Southern Cross is shown on the flag in white. It is a constellation of five stars that can only be seen from the southern hemisphere and is a reminder of Australia’s geography.
Other Countries If your country is not listed here, please research and add the info here. The history of national flags is easy to find online.
Please listen to the Video for the needed information for the worksheet.
|
||||||||||
About Me | Contact Me | Site Map
Property of Mr. D - 2023